Risk scores overestimated risk for CVD in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
- Tanner, Michael MD, FACP
Question
In patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, how do 5 diabetes-specific cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk scores compare with QRISK2 for predicting 5-year risk for CVD?
Methods
Design
Cohort study with a median 5 years of follow-up.
Setting
Population-based study in Scotland.
Patients
181 399 patients 30 to 89 years of age (mean age 60 y, 54% men) who were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes between Jan 2004 and Jun 2016 and had no history of CVD.
Description of prediction guides
Prediction scores were QRISK2; Swedish National Diabetes Register (NDR); Action in Diabetes and Vascular disease: preterAx and diamicroN-MR Controlled Evaluation (ADVANCE) CVD; Fremantle Diabetes Study; New Zealand Diabetes Cohort study (NZ DC); and Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS) risk scores. Scores included combinations of the following predictors: age, sex, ethnicity, diabetes status, diabetes duration, Townsend deprivation score, systolic blood pressure (SBP), pulse pressure, smoking status, body mass index, total-to-high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, glycated hemoglobin, retinopathy, rheumatoid arthritis, atrial fibrillation, chronic kidney disease, micro- and macroalbuminuria, albumin-to-creatinine ratio, creatinine, family history of CVD; and glucose-lowering, antihypertensive, or lipid-lowering medications. Data were obtained from the Scottish Care Information–Diabetes database; proxy predictors were used for variables not included in the database.
Outcome
CVD (hospital admission or death from myocardial infarction; stroke; unstable angina; transient ischemic attack; peripheral vascular disease; or coronary, carotid, or major amputation procedures) determined from linkage with the Scottish Morbidity Record.
Main results
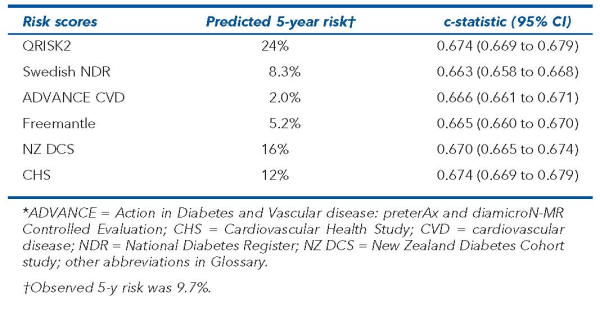
14 081 incident CVD events occurred during the study. Observed 5-year risk for CVD was 9.7% (95% CI 9.6 to 9.9). The main results are in the Table.
Conclusion
In newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, 6 diabetes-specific cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk scores, including QRISK2, poorly predicted 5-year risk for CVD (c-statistics < 0.68).