Abstract 20505
In vivo Imaging of Vesicles Loaded with Near Infrared Dye Targeted to CD44 on Inflamed Endothelial Cells in a Mouse Model of Atherosclerosis
- Elliott, John A
- Muffly, Karl
- Strom, Joel A
- Flam, Brenda R
Introduction: CD44, an adhesion molecule overexpressed in atherosclerosis, provides a site for targeted drug delivery. We hypothesized that our novel surfactant vesicle loaded with near infrared dye (IRDye-800CW) and conjugated with anti-CD44 antibodies can target dysfunctional endothelium in the apoE −/− mouse and can increase vesicle circulation time.
Methods: First, using polyethylene glycol (PEG)-modified nonionic surfactant vesicles conjugated with anti-CD44 antibodies (immuno-niosomes, CD44-INs), we demonstrated surface binding to and internal delivery of a payload to TNFα-activated endothelial cells. Next, apoE −/− mice (n=6), fed a high fat diet for 31 or 38 d, or control C57BL/6J mice (n=2), fed a normal chow diet, were intravenously injected with 0.5 nmol IRDye-800CW-PEG-CD44-INs. Whole body epi-fluorescent imaging was performed using an IVIS 200 Spectrum small animal imager on d 31 at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 26 and 52 h post-injection. Whole body imaging was performed on d 38 at 0, 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 h post-injection. Organs were imaged ex vivo at the 1, 2 and 4 h time points (n=2/time point).
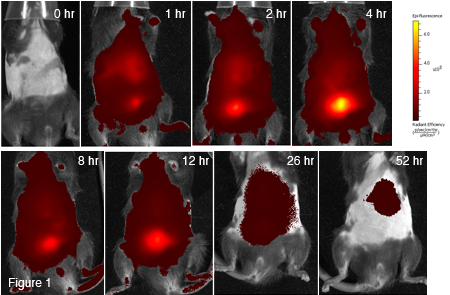
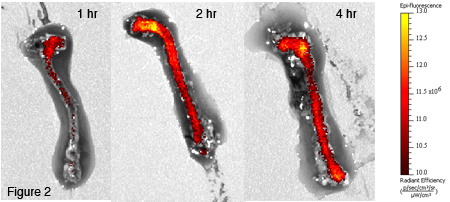
Results: Extended vesicle circulation time in an apoE −/− mouse at 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 26 and 52 h was observed (Figure 1). At 1, 2 and 4 h post-injection, aorta bound IRDye-800CW-PEG-CD44-INs were visualized (Figure 2).
Conclusions: Preliminary results indicate our ability to target inflamed aortic endothelial cells in an atherosclerotic mouse using a vesicle with extended circulation time. This CD44 vesicle design represents a valuable tool for: 1) imaging atherosclerotic plaques and 2) targeting encapsulated therapeutic agents to areas of inflammation.
Figure
No caption available.
Figure
No caption available.
