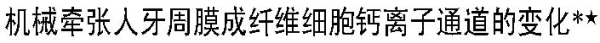SymbolChanges in calcium ion channel of human periodontal fibroblasts under mechanical strain
- Sun, Miao
- Zhang, Miao-miao
- Shao, Ming
- Dai, Jia-yin
- Ni, Hui
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
The mechanical strain can result in changes of cell function via alter the calcium concentration by activating calcium channel.
OBJECTIVE:
To investigate the influence of the calcium channel changes under mechanical strain by using confocal laser microscopy.
DESIGN, TIME AND SETTING:
The cell experiment was performed at the Harbin Medical University College of Pharmacy between March 2007 and August 2008.
MATERIALS:
Nifedipine and cadmium chloride were purchased from American SIGMA Company. The premolars were extracted from 12 to 16 years old teenagers.
METHODS:
Human periodontal ligament fibroblasts (PDLF) were cultured with enzymatic digestion method, and then the cells were subjected to mechanical strain of 8%, 12%, after 2 hours and 4 hours, each group was added 10 or 20 µm nifedipine and 10 µm cadmium chloride, especially, Meantime, the normal and control group was performed, in total, there were 17 groups in the experiment. After loaded by Fluo-3/AM, laser scanning confocal microscope was used to investigate the changes of fluorescence intensity of HPDLFs under different strain time and elastic deformation.
MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES:
Changes of fluorescence intensity, as well as calcium concentration was determined by laser scanning confocal microscope.
RESULTS:
The calcium concentration of HPDLFs was obvious increased in the single strain group, with greatly enhanced brightness of cells. After adding with 10, 20 µmol nifedipine, as the increasing drug concentration, the brightness of cells were gradually weakened, which was more significantly after cadmium chloride was added. The calcium concentration of HPDLFs was notably increased at the 8% deformation with 2 hours strain group (P < 0.01), which gradually lowered after adding with 10, 20 µmol nifedipine (P < 0.01), but remained higher than the control group. The decreasing of calcium concentration was more significantly than that of the cadmium chloride group (P < 0.01), which remained higher than the normal group. The results of 8% deformation with 4 hours strain, 12% deformation with 2 hours strain, and 12% deformation with 4 hours strain group was consistent with 8% deformation with 2 hours strain group.
CONCLUSION:
Tension-force can increase the calcium concentrationl of HPDLFs, which is irrelevant to ausform or strain times. Nifedipine and the calcium chloride can decrease the calcium concentration, especially stronger in cadmium chloride.
Sun M, Zhang MM, Shao M, Dai JY, Ni H. Changes in calcium ion channel of human periodontal fibroblasts under mechanical strain.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(33): 6523-6526. [http://http://www.crter.cn http://en.zglckf.com]

Symbol
No caption available.