Low dose combination treatment increases efficacy of blood pressure lowering drugs and reduces adverse effects
- Weber, Michael A. MD
BACKGROUND
The risk of stroke and ischaemic heart disease at age 65 can be significantly reduced by lowering blood pressure. The safest and most effective dosage of the five main classes of blood pressure lowering drugs (thiazides, β-blockers, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists and calcium channel blockers), whether singly or in combination with another drug, is yet to be determined.
OBJECTIVE
To assess the efficacy and safety of the primary classes of blood pressure lowering drugs.
METHOD
Systematic review with meta-analysis.
SEARCH STRATEGY
MEDLINE (1966 to 2000), Cochrane Library and Web of Science; hand searches of bibliographies and contact with pharmaceutical companies.
INCLUSION/EXCLUSION CRITERIA
Eligible studies were English language, randomized controlled trials assessing changes in blood pressure in response to specified doses of thiazide, β-blocker, ACE inhibitor, angiotensin II receptor antagonist or calcium channel blocker. Main exclusion criteria: no placebo group, <2 weeks duration; testing drugs only in combination with other drugs, or in people with heart failure, acute myocardial infarction or other cardiovascular disorders.
OUTCOMES
Reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure; adverse effects.
MAIN RESULTS
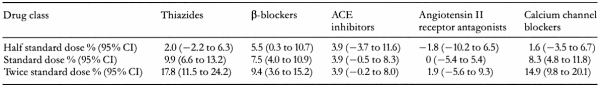
Three hundred and fifty four randomised trials (56,000 people) met inclusion criteria. Single drugs: At any given dose, no single class of drug was significantly more effective at lowering blood pressure than another. Combination drugs: One hundred and nineteen RCTs compared two different drugs with each drug alone. Six of 10 possible combinations of drug classes acted additively to reduce blood pressure. Adverse effects: No drug class was consistently more likely to produce adverse effects than any other class across three different doses (see Table 1). There was no additive effect of adverse effects when drugs were used in combination.
AUTHORS' CONCLUSIONS
When used alone, the five drug classes are similarly safe and effective at lowering blood pressure. The efficacy of drugs used in combination was additive, and reduced the incidence of adverse effects.